Building a data warehouse in the cloud using Snowflake
The continued presence of on-premises data warehouses represents an increasing burden given it requires complex integrations comprising of both code and infrastructure [1]. When most of a company’s assets are in the cloud, establishing and maintaining data warehousing processes is vital for a business's success.
Building a data warehouse in the cloud using Snowflake can help companies of all sizes move to a modern cloud data warehouse.
Model of Snowflake warehouse
Snowflake as the data warehouse home
What is Snowflake?
Snowflake is a parallel processing data environment that lives in the cloud. In context of this article, Snowflake is the housed location for the data warehouse and all data warehouse related activities.
Benefits of Snowflake
Speed
- Snowflake has customizable warehouses (compute nodes) that can be adjusted to fit the volume of data as needed, allowing for speedy updates to the data warehouse
- Querying Snowflake from a reporting tool is quite fast, enabling users to quickly gain data insights from the model
- Querying can be improved by establishing partitioning practices to allow Snowflake to prune queries for better performance [2]
Administration
- Administration of Snowflake is easily manageable and accessible, allowing more time to distribute the data to the business
Connectivity
- Snowflake can connect to different cloud service providers to capture data from the business
- Snowflake also offers a variety of connections to different tools to allow for visualization and analysis, including but not limited to Power BI, Analysis Services, Python and C#
Security
- Security is robust and implementable on many levels to expose the data only to the parts of a business that specifically needs it
- Snowflake can expose data via direct connection from a reporting service, allowing for row-level security. It also can provide read-only accounts for exposing specific databases for different parts of the business [3]
Collaboration
- Snowsight, the Snowflake web interface, provides a collaborative workspace as worksheets can be easily shared between members of the business, stored under folders and utilized to help implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices [4]
- Snowsight also offers easy ways to access the tools used in a data warehouse as well as setting up dashboards for quick analysis of important data points
Historical Data
- Snowflake retains historical data to provide the ability to view snapshots of data from the past [5], giving a business the ability to look back in time or revert data to an older state
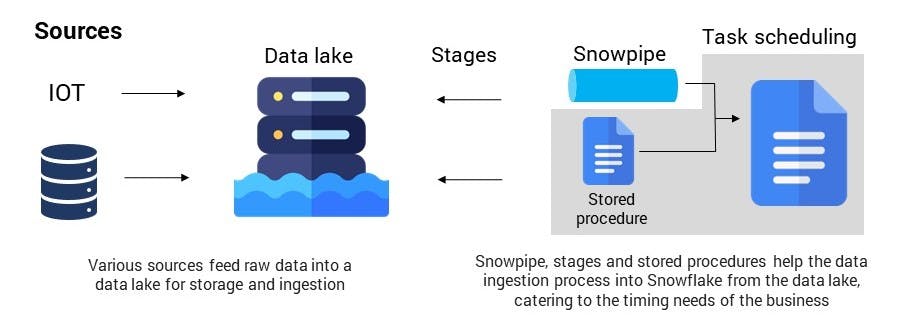
Data lake for source data organization in Snowflake
Snowflake and data lakes
Snowflake offers a variety of ways to connect to raw data files including files from local storage or external cloud storage services.
Using Snowflake stages, a business can seamlessly upload data into tables in Snowflake using the [COPY INTO] command. The [COPY INTO] command offers a variety of customizable options, such as pattern matching, specific file formatting and incremental loading, that allows for businesses to easily transition data from the raw files to staging tables for use in the data warehouse.
Automating data loads using Snowflake
When looking to automate data loads into Snowflake, there are two viable options:
Stored procedures
In Snowflake, stored procedures can utilize JavaScript to dynamically create and execute [COPY INTO] statements. Combined with a metadata framework, businesses can have tight control over when staging tables are updated with the latest data.
Snowflake pipes (Snowpipe)
- Snowpipes are connected to stages that execute a single [COPY INTO] statement [6]. The benefit of Snowpipe is derived from its ability to auto ingest data as it lands in the data lake, allowing for more real-time ingestion of data into Snowflake and the staging tables. (Note: auto ingest cannot be used for internal stages. To use Snowpipe for internal stages, a [REST API] endpoint must be called).
A cloud data warehouse in Snowflake will likely utilize a combination of the two loading options, using stored procedures to load files once a day and Snowpipes to ingest data as it lands in the external stage (like streaming data) to reduce overall load times into the associated staging tables.
Using streams to identify new data
Snowflake’s stream feature allows for new (and deleted) rows to be tracked regarding the table they are assigned to. While the [COPY INTO] command will only upload new files, the associated streams can then identify the exact changes that occurred.
Streams are much like tables and can be queried as such, which means that the data warehouse processes can utilize them to incrementally update the data in the dimensional model. When a Data Manipulation Language (DML) statement is executed against them, the rows are removed from the stream.
Incorporating streams in the data warehouse is essential for having a fast-performing extract, transform and load (ETL) cycle when dealing with large volumes of data.
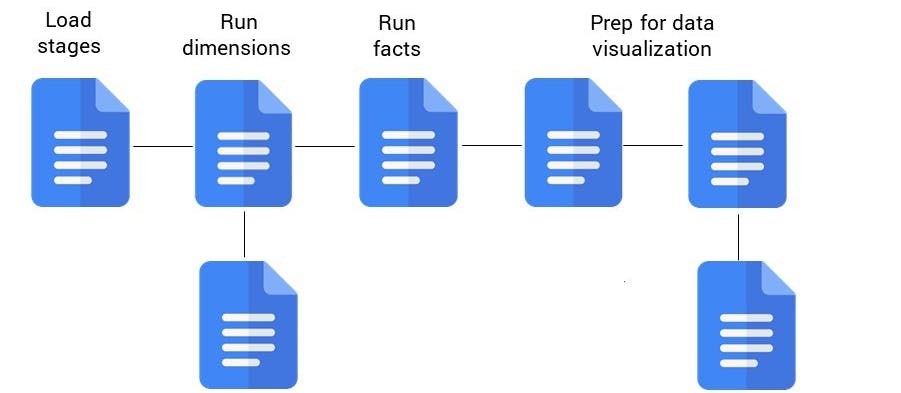
Using tasks for orchestration in Snowflake
General architecture
What is a task?
A task in Snowflake is a defined SQL statement or call to stored procedure that can be set to execute at specific times or after other tasks.
By using tasks, a business can create directed acrylic graphs (DAGs) of the SQL statements needed to load the data into the staging tables, transform the data as needed and update the tables in the data warehouse [7].
Tasks offer a variety of settings to align with the needs of the data warehouse such as:
- Scheduling can be set for specific days and times or set to run as specified intervals, enabling more real time data if needed
- Tasks can check for the existence of new data in specified streams to determine whether they should execute
Usage of tasks in Snowflake is the backbone of building the data warehouse, enabling automated processes.
How we can help
A well-constructed data warehouse is a key asset to the data-driven business. Building a data warehouse in the cloud using Snowflake enables businesses to reap the benefits of proven methodologies while scaling for continued growth. Utilizing the techniques described in this article will allow a business to support and enhance analytics as they shift to using Snowflake.
As a Snowflake Select Partner, Baker Tilly helps businesses optimize the performance, security, shareability and scale of their cloud data warehouse. Our practice professionals work with you, providing informed perspectives, to uncover and solve the digital challenges your business is facing, so you can work to build more meaningful relationships with your next generation of customers.
Interested in learning more?